Kong Gateway and proxy_protocol on AWS EKS
This post will help you take advantage of proxy_protocol to preserve the client IP address with Kong on Kubernetes.

This post will help you take advantage of proxy_protocol to preserve the client IP address with Kong on Kubernetes. I've been using Terraform to deploy Kong's API Gateway on AWS EKS. You can go look at that deployment code here. The code up to now goes with the Kubernetes-driven way to configure Kong's API Gateway, using the Kong Ingress controller's custom resources. I prefer YAML driven config for this case, especially on Kubernetes when everything else is YAML driven anyway, and it comes with the bonus of not having to manage a separate PostgreSQL database somewhere.
However, quite often the companies I work with want Kong's GUI installed, and the database, and Kong's Admin API available, and the Developer Portal etc. You know, take advantage of all the things they paid for. When deploying Kong on Kubernetes with all the things, I also like to put all of Kong's internal services behind Kong's Gateway. It saves on load balancer cost and allows you to apply Kong plugins easily to Kong's own stuff.
Having said ALL THAT, when deploying to Amazon EKS, Kong recommends an Network Load Balancer in front of Kong's proxy (the gateway). NLBs can do TLS termination now, which is SWEET because it's one less thing to manage. Thanks, Amazon, handle my certs for me, I care not how. Using a Load Balancer in front of Kong means you want to get the client's actual IP address for your client requests instead of the load balancer IP in your logs. Kong has documentation on this but actual code is more fun. What happens is AWS gets your client request, terminates TLS, and then adds headers to the request before passing it to Kong. If you want to get deep into proxy_protocol you can read all about it. Again, I use helm to drive my deployments, so here's the helm values file to use to take advantage of proxy_protocol. To use this you'll need to have some secrets in place and a namespace for Kong (in my case "kong").
image:
repository: kong/kong-gateway
tag: "2.6.0.0-alpine"
env:
prefix: /kong_prefix/
nginx_worker_processes: "auto"
anonymous_reports: off
database: postgres
pg_user: kong
pg_password: kong
plugins: bundled
admin_api_uri: https://adminapi.domain.com
admin_gui_url: https://manager.domain.com
portal_api_url: https://portalapi.domain.com
portal_gui_host: portal.domain.com
portal_gui_protocol: https
portal_session_conf:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kong-session-config
key: portal_session_conf
password:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kong-enterprise-superuser-password
key: password
trusted_ips: 0.0.0.0/0,::/0
real_ip_header: proxy_protocol
enterprise:
enabled: true
license_secret: kong-enterprise-license
vitals:
enabled: true
portal:
enabled: true
rbac:
enabled: true
admin_gui_auth: basic-auth
session_conf_secret: kong-session-config
smtp:
enabled: false
admin:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
annotations:
konghq.com/protocol: "http"
http:
enabled: true
servicePort: 8001
containerPort: 8001
parameters: []
tls:
enabled: false
servicePort: 8444
containerPort: 8444
parameters:
- http2
ingress:
enabled: true
hostname: adminapi.domain.com
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "kong"
path: /
manager:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
annotations:
konghq.com/protocol: "http"
http:
enabled: true
servicePort: 8002
containerPort: 8002
parameters: []
tls:
enabled: false
servicePort: 8445
containerPort: 8445
parameters: []
ingress:
enabled: true
hostname: manager.domain.com
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "kong"
path: /
portal:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
annotations:
konghq.com/protocol: "http"
http:
enabled: true
servicePort: 8003
containerPort: 8003
parameters: []
tls:
enabled: false
servicePort: 8446
containerPort: 8446
parameters:
- http2
ingress:
enabled: true
hostname: portal.domain.com
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "kong"
path: /
portalapi:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
annotations:
konghq.com/protocol: "http"
http:
enabled: true
servicePort: 8004
containerPort: 8004
parameters: []
tls:
enabled: false
servicePort: 8447
containerPort: 8447
parameters:
- http2
ingress:
enabled: true
hostname: portalapi.domain.com
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "kong"
path: /
proxy:
enabled: true
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
annotations: {
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol": "tcp",
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-cross-zone-load-balancing-enabled": "true",
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-cert": "arn:aws:acm:us-west-2:XXXXXXXX:certificate/XXXXXX-XXXXXXX-XXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX",
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-ports": "kong-proxy-tls",
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type": "nlb",
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-proxy-protocol": "*"
}
http:
enabled: true
servicePort: 80
containerPort: 8000
parameters:
- proxy_protocol
tls:
enabled: true
servicePort: 443
overrideServiceTargetPort: 8000
containerPort: 8443
parameters:
- proxy_protocol
stream: {}
ingress:
enabled: false
ingressController:
enabled: true
installCRDs: false
env:
kong_admin_token:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kong-enterprise-superuser-password
key: password
# Specify Kong status listener configuration
# This listen is internal-only. It cannot be exposed through a service or ingress.
status:
enabled: true
http:
# Enable plaintext HTTP listen for the status listen
enabled: true
containerPort: 8100
parameters: []
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
# interval: 10s
# Specifies namespace, where ServiceMonitor should be installed
namespace: kong
postgresql:
enabled: true
postgresqlUsername: kong
postgresqlDatabase: kong
postgresqlPassword: kong
service:
port: 5432
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 5
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 80
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 256Mi
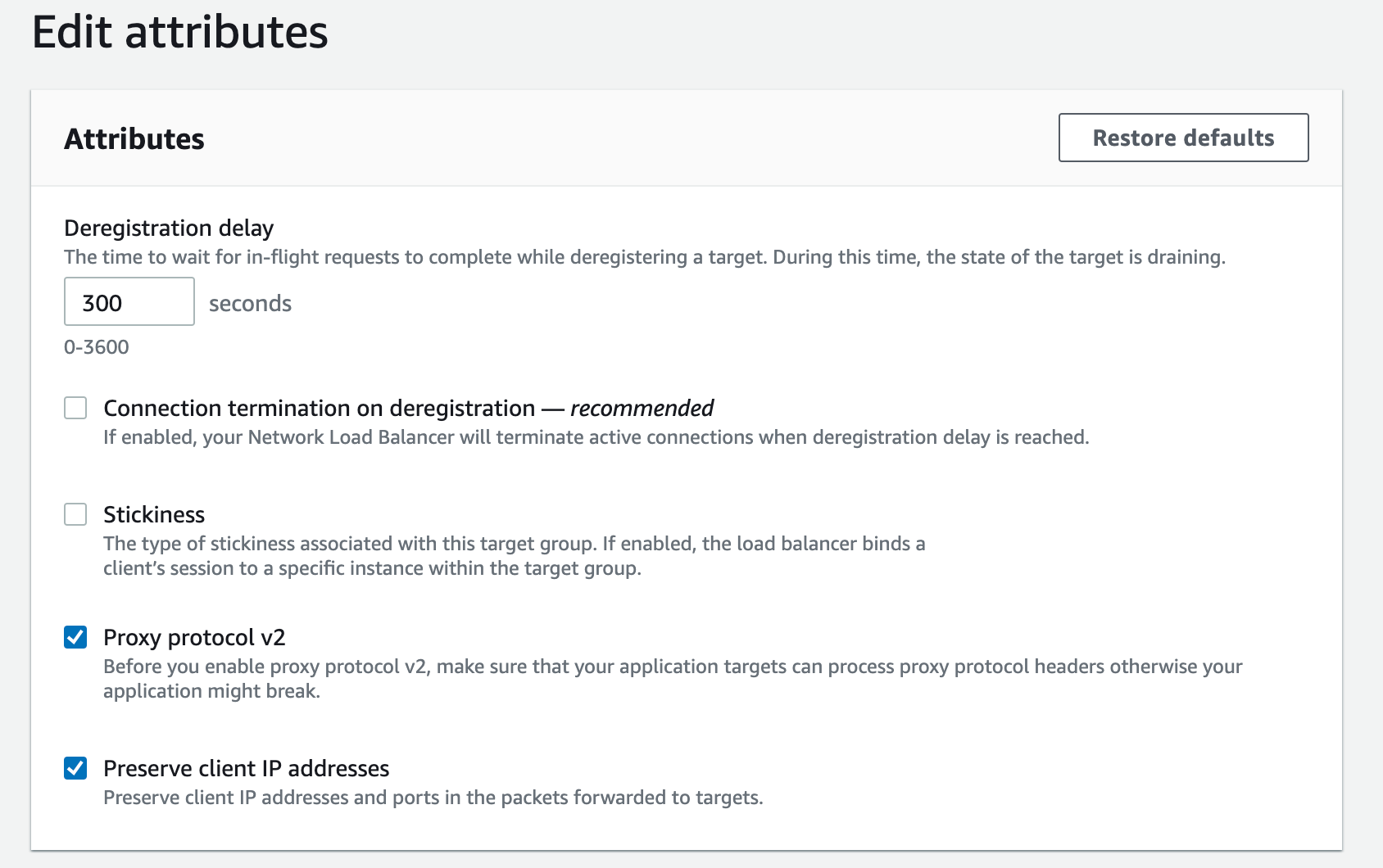
The downside: without the AWS Load Balancer Controller, you can't use an annotation to actually enable proxy_protocol on your target groups. So you can either also install the AWS Load Balancer Controller to have AWS use your NLB target group annotations OR you can log into the AWS Console or use the API to enable "Proxy Protocol v2" on your new Kong Gateway Proxy NLB's target groups like so:
Disclaimer: none of the above is supported by Kong, its partners, or me AT ALL. Use at your own risk. My views do not reflect those of my employer.
